Publication of the research results of University of Tehran professor about desalination of sea water in Elsevier
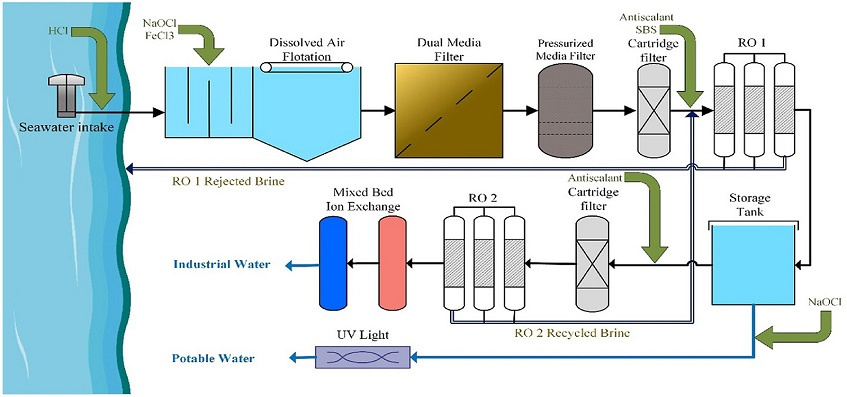
According to the Public Relations report of University of Tehran, the results of the research of Dr. Mazaher Moinedini, a member of the School of Natural Resources, University of Tehran, regarding the Life Cycle Assessment of industrial and drinking water production through desalination of sea water in the form of a joint article in "Cleaner Production" magazine was published by Elsevier.
Dr. Moin Aldini said about the necessity of conducting this research: One of the necessities of industrial development is the provision of water needed for industrial and drinking purposes; in a way that has the least environmental consequences. Seawater desalination is a well-known solution for water supply worldwide, especially in countries with limited water resources such as the Persian Gulf countries. However, the assessment of the environmental consequences of seawater desalination in the Persian Gulf has not been comprehensively done so far.
The faculty member of the School of Natural Resources of University of Tehran added: Therefore, due to the fundamental changes in environmental conditions, the need for an innovative approach in the design and implementation of environmental management system programs based on environmental consequences is felt. On the other hand, one of the leading perspectives on environmental conditions is the perspective of sustainability, and one of the important tools for measuring the state of sustainability is the life cycle assessment method of products and services.
Explaining the findings of the research published in Elsevier Publishing's "Cleaner Production" magazine, Dr. Mazaher Moinedini said: In this article, the environmental consequences of industrial and drinking water production were evaluated based on the life cycle perspective (LCA) and the environmental indicators of Such as global warming, cumulative energy demand, waste of resources for producing one cubic meter of industrial and drinking water from sea water.
This research was jointly conducted by a faculty member of University of Tehran and researchers from Arak University, Southern University of Denmark, Technical University of Denmark, Pardis Petrochemical University and Tarbiat Modares University, and the resulting article is available through the following link:

Your Comment :